The Class is an important year in a student's life and this subject requires dedication, hard work, and practice. It's a subject where you can score well if you are well-versed with the concepts, remember the important formulas and solving methods, and have done an ample amount of practice. Worry not! Home Revise is here to make your journey even easier. It's essential for students to have the right study material and notes to prepare for their board examinations, and through Home Revise, you can cover all the fundamental topics in the subject and the complete syllabus.
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials are provided here to help the students in learning efficiently for their exams. The subject experts of Maths have prepared these solutions to help students prepare well for their exams. They solve these solutions in such a way that it becomes easier for students to practise the questions of Chapter 2 Polynomials using the Solutions of NCERT. This makes it simple for the students to learn by adding step-wise explanations to these Maths NCERT Class 10 Solutions.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths is an extremely important study resource for students. Solving these Polynomials NCERT solutions of Class 10 Maths would help the students fetch good marks in board exams. Also, following the NCERT guidelines is focused on while preparing these solutions.
1. Divide the polynomial p(x) by the polynomial g(x) and find the quotient and remainder in each of the following:
(i) p(x) = x3-3x2+5x–3 , g(x) = x2–2
Solution:
Given,
Dividend = p(x) = x3-3x2+5x–3
Divisor = g(x) = x2– 2
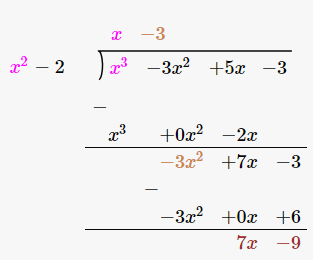
Therefore, upon division we get,
Quotient = x–3
Remainder = 7x–9
(ii) p(x) = x4-3x2+4x+5 , g(x) = x2+1-x
Solution:
Given,
Dividend = p(x) = x4 – 3x2 + 4x +5
Divisor = g(x) = x2 +1-x
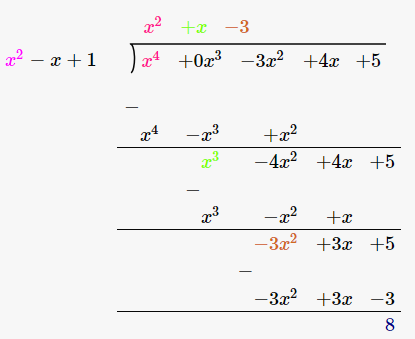
Therefore, upon division we get,
Quotient = x2 + x–3
Remainder = 8
(iii) p(x) =x4–5x+6, g(x) = 2–x2
Solution:
Given,
Dividend = p(x) =x4 – 5x + 6 = x4 +0x2–5x+6
Divisor = g(x) = 2–x2 = –x2+2
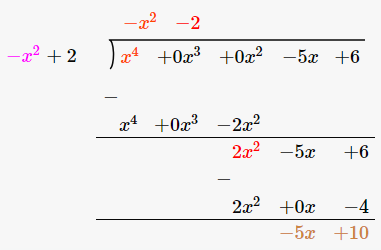
Therefore, upon division we get,
Quotient = -x2-2
Remainder = -5x + 10
2. Check whether the first polynomial is a factor of the second polynomial by dividing the second polynomial by the first polynomial:
(i) t2-3, 2t4 +3t3-2t2-9t-12
Solutions:
Given,
First polynomial = t2-3
Second polynomial = 2t4 +3t3-2t2 -9t-12
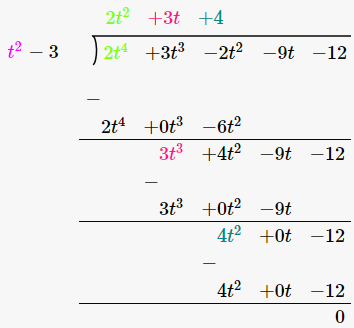
As we can see, the remainder is left as 0. Therefore, we say that, t2-3 is a factor of 2t2+3t+4.
(ii)x2+3x+1 , 3x4+5x3-7x2+2x+2
Solutions:
Given,
First polynomial = x2+3x+1
Second polynomial = 3x4+5x3-7x2+2x+2
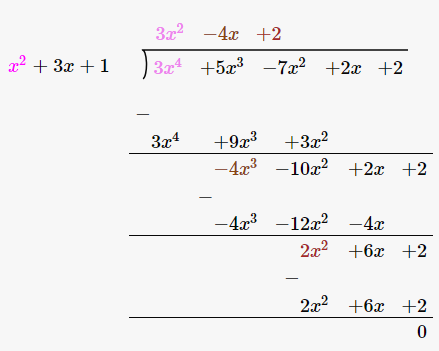
As we can see, the remainder is left as 0. Therefore, we say that, x2 + 3x + 1 is a factor of 3x4+5x3-7x2+2x+2.
(iii) x3-3x+1, x5-4x3+x2+3x+1
Solutions:
Given,
First polynomial = x3-3x+1
Second polynomial = x5-4x3+x2+3x+1
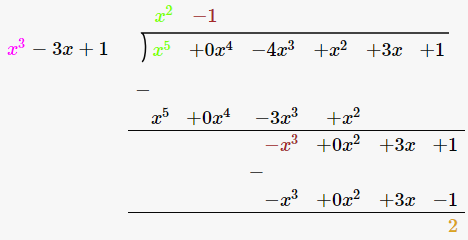
As we can see, the remainder is not equal to 0. Therefore, we say that, x3-3x+1 is not a factor of x5-4x3+x2+3x+1 .
3. Obtain all other zeroes of 3x4+6x3-2x2-10x-5, if two of its zeroes are √(5/3) and – √(5/3).
Solutions:
Since this is a polynomial equation of degree 4, hence there will be total 4 roots.
√(5/3) and – √(5/3) are zeroes of polynomial f(x).
∴ (x –√(5/3)) (x+√(5/3) = x2-(5/3) = 0
(3x2−5)=0, is a factor of given polynomial f(x).
Now, when we will divide f(x) by (3x2−5) the quotient obtained will also be a factor of f(x) and the remainder will be 0.
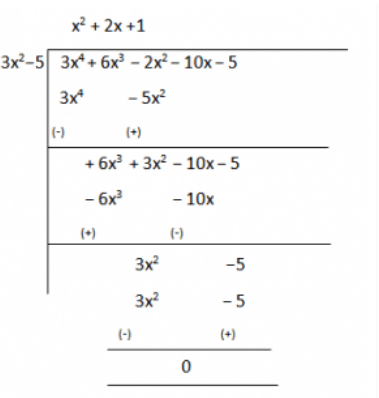
Therefore, 3x4 +6x3 −2x2 −10x–5 = (3x2 –5)(x2+2x+1)
Now, on further factorizing (x2+2x+1) we get,
x2+2x+1 = x2+x+x+1 = 0
x(x+1)+1(x+1) = 0
(x+1)(x+1) = 0
So, its zeroes are given by: x= −1 and x = −1.
Therefore, all four zeroes of given polynomial equation are:
√(5/3),- √(5/3) , −1 and −1.
Hence, is the answer.
4. On dividing x3-3x2+x+2 by a polynomial g(x), the quotient and remainder were x–2 and –2x+4, respectively. Find g(x).
Solution:
Given,
Dividend, p(x) = x3-3x2+x+2
Quotient = x-2
Remainder = –2x+4
We have to find the value of Divisor, g(x) =?
As we know,
Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
∴ x3-3x2+x+2 = g(x)×(x-2) + (-2x+4)
x3-3x2+x+2-(-2x+4) = g(x)×(x-2)
Therefore, g(x) × (x-2) = x3-3x2+x+2
Now, for finding g(x) we will divide x3-3x2+x+2 with (x-2)
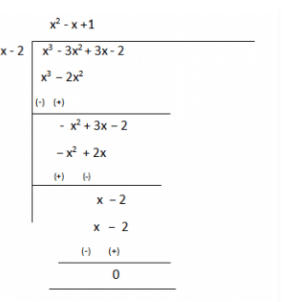
Therefore, g(x) = (x2–x+1)
5. Give examples of polynomials p(x), g(x), q(x) and r(x), which satisfy the division algorithm and
(i) deg p(x) = deg q(x)
(ii) deg q(x) = deg r(x)
(iii) deg r(x) = 0
Solutions:
According to the division algorithm, dividend p(x) and divisor g(x) are two polynomials, where g(x)≠0. Then we can find the value of quotient q(x) and remainder r(x), with the help of below given formula;
Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
∴ p(x) = g(x)×q(x)+r(x)
Where r(x) = 0 or degree of r(x)< degree of g(x).
Now let us proof the three given cases as per division algorithm by taking examples for each.
(i) deg p(x) = deg q(x)
Degree of dividend is equal to degree of quotient, only when the divisor is a constant term.
Let us take an example, 3x2+3x+3 is a polynomial to be divided by 3.
So, (3x2+3x+3)/3 = x2+x+1 = q(x)
Thus, you can see, the degree of quotient is equal to the degree of dividend.
Hence, division algorithm is satisfied here.
(ii) deg q(x) = deg r(x)
Let us take an example , p(x)=x2+x is a polynomial to be divided by g(x)=x.
So, (x2+x)/x = x+1 = q(x)
Also, remainder, r(x) = 0
Thus, you can see, the degree of quotient is equal to the degree of remainder.
Hence, division algorithm is satisfied here.
(iii) deg r(x) = 0
The degree of remainder is 0 only when the remainder left after division algorithm is constant.
Let us take an example, p(x) = x2+1 is a polynomial to be divided by g(x)=x.
So,( x2+1)/x= x=q(x)
And r(x)=1
Clearly, the degree of remainder here is 0.
Hence, division algorithm is satisfied here.
